LeRobot Dataset
LeRobot is an open-source robotic learning data standardization framework by Hugging Face, specifically designed for robotic learning and reinforcement learning scenarios. It provides a unified data format specification, enabling researchers to more easily share, compare, and reproduce robotic learning experiments, significantly reducing the cost of data format conversion between different research projects.
Exporting Data
The diagram below summarizes the path from annotated data to model training: choose export format, configure parameters, export and download, then use with LeRobot or OpenPI to train Pi0, SmolVLA, ACT, and other models.
The EmbodiFlow platform fully supports exporting data in the LeRobot standard format, which can be directly used in the training workflow for VLA (Vision-Language-Action) models. The exported data contains complete multi-modal information of robot operations: visual perception data, natural language instructions, and corresponding action sequences, forming a complete perception-understanding-execution closed-loop data mapping.
Exporting data in LeRobot format requires high computational resources. The free version of the EmbodiFlow platform has reasonable limits on the number of exports per user, while the paid version offers unlimited export services and is equipped with GPU acceleration to significantly speed up the process.
1. Selecting Data for Export
Data annotation must be completed before exporting. The annotation process creates a precise mapping between the robot's action sequences and corresponding natural language instructions, which is a prerequisite for training VLA models. Through this mapping, the model learns to understand language commands and translate them into accurate robot control actions.
For detailed workflows and batch annotation tips, please refer to the Data Annotation Guide.
Once annotation is complete, you can view all annotated datasets in the export interface. The system supports flexible data subset selection, allowing you to choose specific data for export based on your needs.

Dataset naming supports custom settings. If you plan to publish the dataset to the Hugging Face platform, it is recommended to use the standard repository naming format (e.g., myproject/myrepo1), which facilitates subsequent model sharing and collaboration.
Export Configuration Options
In the configuration panel on the right side of the export interface, you can set the following export parameters:
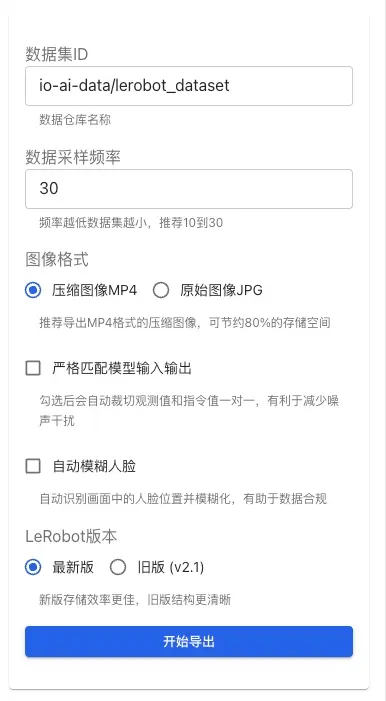
Data Sampling Frequency: Controls the frequency of data sampling (recommended 10-30 Hz). Lower frequencies result in smaller datasets but may lose some detailed information.
Image Format:
- MP4 (Recommended): Compressed image format, saving about 80% of storage space, suitable for large-scale dataset exports.
- JPG: Original image format, preserving full image quality but with larger file sizes.
Strictly Match Model Input/Output: When enabled, the system automatically crops observations and instructions to ensure a one-to-one correspondence, helping reduce noise interference and improving training data quality.
Auto Blur Faces: When enabled, the system automatically identifies face positions in the frames and applies blurring. This feature helps:
- Protect personal privacy and comply with data compliance requirements.
- Suitable for datasets containing footage of operators.
- Automatically handles face information in all exported images.
Larger data volumes take longer to export. It is recommended to export by task type to avoid processing all data at once. Batch exporting not only speeds up processing but also facilitates subsequent data management, version control, and targeted model training.
2. Downloading and Unzipping Exported Files
The time required for export depends on the scale of data and current system load, typically taking tens of minutes. The page will automatically update the progress status; you can return later to check the results.
Once the export is complete, a Download Data button will appear in the Export History area on the right side of the page. Clicking it will provide a .tar.gz compressed file package.
It is recommended to create a dedicated directory locally (e.g., ~/Downloads/mylerobot3) to unzip the files to avoid confusion with other data:
The unzipped files strictly follow the LeRobot dataset standard format specifications, containing complete multi-modal data: visual perception data, robot state information, and action labels, etc.:
3. Custom Topic Mapping
When exporting a LeRobot dataset, the system needs to map ROS/ROS2 topics to the observation.state and action fields in the LeRobot standard format. Understanding topic mapping rules is crucial for correctly exporting custom datasets.
Default Topic Mapping Rules
The EmbodiFlow platform uses an automatic recognition mechanism based on topic name suffixes:
Observation (observation.state) Mapping Rules:
- When a topic name ends with
/joint_stateor/joint_states, the system automatically recognizes itspositionfield value as an observation and maps it to theobservation.statefield. - For example:
io_teleop/joint_states,/arm/joint_state, etc., will be recognized as observations.
Action (action) Mapping Rules:
- When a topic name ends with
/joint_cmdor/joint_command, the system automatically recognizes itspositionfield value as an action command and maps it to theactionfield. - For example:
io_teleop/joint_cmd,/arm/joint_command, etc., will be recognized as action values.
To ensure data can be exported correctly, it is recommended to follow the naming conventions above when recording data. If your robot system uses a different naming style, you can contact the technical support team for adaptation.
Custom Topic Support
If you have built custom topics that do not follow the default rules above, you can handle them in the following ways:
-
Rename Topics: During the data recording phase, rename custom topics to names that comply with the default rules (e.g.,
/joint_statesor/joint_command). -
Contact Technical Support: If topic names cannot be modified, you can contact the EmbodiFlow technical support team. We will adapt to your specific naming style to ensure data can be correctly mapped to the LeRobot format.
The current version does not support specifying custom topic mappings directly in the export interface. If you have special requirements, it is recommended to communicate with the technical support team in advance, and we will complete the corresponding configuration adaptation before export.
Data Visualization and Verification
To help users quickly understand and verify data content, LeRobot provides various data visualization solutions. Each has its own application scenarios and unique advantages, with LeRobot Studio being the recommended choice on the EmbodiFlow platform:
| Usage Scenario | Visualization Solution | Key Advantages |
|---|---|---|
| Quick Privacy Preview (Recommended) | LeRobot Studio (Web) | No installation, no upload, privacy protection, drag & drop |
| Local Development & Debugging | Rerun SDK Local View | Full functionality, highly interactive, offline available |
| Public Sharing & Showcase | Hugging Face Online View | Community collaboration, easy sharing, accessible anytime |
1. Online Visualization with LeRobot Studio (Recommended)
The EmbodiFlow platform provides a natively integrated LeRobot visualization tool — LeRobot Studio. This is currently the most convenient data preview solution. You do not need to install any local environment or upload data to Hugging Face. You can complete rapid visualization and verification of local data directly in your browser.
Online Experience Address: https://io-ai.tech/lerobot/
Core Advantages
- Zero Barrier: No Python environment configuration, no Rerun SDK installation required.
- Privacy & Security: Supports direct drag-and-drop preview of local data files. Data is processed locally and does not pass through cloud servers, fully guaranteeing data privacy.
- Seamless Integration: The EmbodiFlow data platform has integrated LeRobot data export and visualization analysis capabilities, available anytime, anywhere.
- Feature Complete: Fully supports multi-modal data playback in standard LeRobot format (images, states, actions).
Usage
- Visit LeRobot Studio.
- Click the "Select File" button on the page or directly drag the exported
.tar.gzdata package (or unzipped folder) into the window. - The system automatically parses the data structure and immediately starts interactive playback.
2. Local Visualization with Rerun SDK
By installing the lerobot repository locally, you can use its built-in lerobot/scripts/visualize_dataset.py script with the Rerun SDK for timeline-based interactive multi-modal data visualization. This method can simultaneously display images, states, actions, and other multi-dimensional information, providing the richest interaction features and customization options.
Environment Preparation and Dependency Installation
Ensure your Python version is 3.10 or higher, then execute the following installation commands:
# Install Rerun SDK
python3 -m pip install rerun-sdk==0.23.1
# Clone LeRobot official repository
git clone https://github.com/huggingface/lerobot.git
cd lerobot
# Install LeRobot development environment
pip install -e .
Starting Data Visualization
python3 -m lerobot.scripts.visualize_dataset \
--repo-id io-ai-data/lerobot_dataset \
--root ~/Downloads/mylerobot3 \
--episode-index 0
Parameter Descriptions:
--repo-id: Hugging Face dataset identifier (e.g.,io-ai-data/lerobot_dataset).--root: Local storage path for the LeRobot dataset, pointing to the unzipped directory.--episode-index: Specifies the episode index number to visualize (starting from 0).
Generating Offline Visualization Files
You can save visualization results as Rerun format files (.rrd) for offline viewing or sharing with team members:
python3 -m lerobot.scripts.visualize_dataset \
--repo-id io-ai-data/lerobot_dataset \
--root ~/Downloads/mylerobot3 \
--episode-index 0 \
--save 1 \
--output-dir ./rrd_out
# Offline view saved visualization file
rerun ./rrd_out/lerobot_pusht_episode_0.rrd
Remote Visualization (WebSocket Mode)
When you need to process data on a remote server but view it locally, you can use the WebSocket connection mode:
# Start visualization service on the server side
python3 -m lerobot.scripts.visualize_dataset \
--repo-id io-ai-data/lerobot_dataset \
--root ~/Downloads/mylerobot3 \
--episode-index 0 \
--mode distant \
--ws-port 9091
# Connect to remote visualization service locally
rerun ws://SERVER_IP_ADDRESS:9091
3. Online Visualization with Hugging Face Spaces
If you don't want to install a local environment, LeRobot provides an online visualization tool based on Hugging Face Spaces that can be used without any local dependencies. This method is especially suitable for quickly previewing data or sharing dataset content with a team.
The online visualization feature requires uploading data to a Hugging Face online repository. Note that free Hugging Face accounts only support visualization for public repositories, meaning your data will be publicly accessible. If your data contains sensitive information and needs to remain private, it is recommended to use the local visualization solution.
Operation Workflow
- Visit the online visualization tool: https://huggingface.co/spaces/lerobot/visualize_dataset
- Enter your dataset identifier in the Dataset Repo ID field (e.g.,
io-intelligence/piper_uncap_pen). - Select the task number to view in the left panel (e.g.,
Episode 0). - Multiple playback options are provided at the top of the page for you to choose the most suitable view.
Model Training Guide
Model training based on the LeRobot dataset is the core link in achieving robot learning. Different model architectures have varying requirements for training parameters and data preprocessing. Choosing the right model strategy is crucial for training results.
Model Selection Strategy
Current mainstream VLA models include:
| Model Type | Application Scenario | Key Features | Recommended Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| smolVLA | Single-GPU environment, rapid prototyping | Moderate parameters, efficient training | Consumer GPUs, Proof of Concept |
| Pi0 / Pi0.5 | Complex tasks, multi-modal fusion | Leading VLA models, strong generalization | Production environments, complex interactions |
| ACT | Single-task optimization | High action prediction accuracy | Specific tasks, high-frequency control |
| Diffusion | Smooth action generation | Diffusion model-based, high trajectory quality | Tasks requiring smooth trajectories |
| VQ-BeT | Action discretization | Vector quantization, fast inference | Real-time control scenarios |
| TDMPC | Model Predictive Control | High sample efficiency, online learning | Data-scarce scenarios |
Fine-tuning of Pi0/Pi0.5 models must use the OpenPI framework. Although data is exported in LeRobot v2.1 format, the training workflow differs from the LeRobot CLI.
For a detailed fine-tuning guide, please refer to: Pi0 and Pi0.5 Model Fine-tuning Guide
smolVLA Training Details (Recommended for Beginners)
smolVLA is a VLA model optimized for consumer-grade/single-GPU environments. Instead of training from scratch, it is highly recommended to fine-tune based on official pre-trained weights, which can significantly shorten training time and improve final results.
LeRobot training commands use the following parameter format:
- Policy Type:
--policy.type smolvla(specifies which model to use) - Parameter Values: Separated by spaces, e.g.,
--batch_size 64(not--batch_size=64) - Boolean Values: Use
true/false, e.g.,--save_checkpoint true - List Values: Separated by spaces, e.g.,
--policy.down_dims 512 1024 2048 - Model Upload: By default, add
--policy.push_to_hub falseto disable automatic upload to Hugging Face Hub.
Environment Preparation
# Clone LeRobot repository
git clone https://github.com/huggingface/lerobot.git
cd lerobot
# Install full environment supporting smolVLA
pip install -e ".[smolvla]"
Fine-tuning Training (Recommended Solution)
- Local datasets are recommended by default: Training data is usually large, and it is recommended to directly use the local unzipped directory.
--dataset.repo_id local/xxx--dataset.root /path/to/dataset(directory should containmeta.json,data/, etc.)
- If you have already uploaded data to Hugging Face Hub: You can just keep
--dataset.repo_id your-name/your-repoand remove--dataset.root.
Local Dataset Fine-tuning Example (Default Recommended)
# Example: Your data is in a local directory (containing meta.json, data/, etc.)
DATASET_ROOT=~/Downloads/mylerobot3
lerobot-train \
--policy.type smolvla \
--policy.pretrained_path lerobot/smolvla_base \
--dataset.repo_id local/mylerobot3 \
--dataset.root ${DATASET_ROOT} \
--output_dir /data/lerobot_smolvla_finetune \
--batch_size 64 \
--steps 20000 \
--policy.optimizer_lr 1e-4 \
--policy.device cuda \
--policy.push_to_hub false \
--save_checkpoint true \
--save_freq 5000
Practical Recommendations:
- Data Preparation: It is recommended to record 50+ task demonstration clips to ensure coverage of different object positions, poses, and environmental changes.
- Training Resources: Training 20k steps on a single A100 takes about 4 hours; consumer-grade GPUs can lower
batch_sizeor enable gradient accumulation. - Hyperparameter Tuning: Start with
batch_size=64,num_train_steps=20k, and a learning rate of1e-4for fine-tuning. - When to train from scratch: Only consider training from scratch with
--policy.type=smolvlaif you have a massive dataset (thousands of hours).
Training from Scratch (Advanced Users)
# Training from scratch (local dataset example)
DATASET_ROOT=~/Downloads/mylerobot3
lerobot-train \
--policy.type smolvla \
--dataset.repo_id local/mylerobot3 \
--dataset.root ${DATASET_ROOT} \
--output_dir /data/lerobot_smolvla_fromscratch \
--batch_size 64 \
--steps 200000 \
--policy.optimizer_lr 1e-4 \
--policy.device cuda \
--policy.push_to_hub false \
--save_checkpoint true \
--save_freq 10000
Performance Optimization Tips
VRAM Optimization:
# Add the following parameters to optimize VRAM usage
--policy.use_amp true \
--num_workers 2 \
--batch_size 32 # Reduce batch size
Training Monitoring:
- Configure Weights & Biases (W&B) to monitor training curves and evaluation metrics.
- Set reasonable validation intervals and early stopping strategies.
- Periodically save checkpoints to prevent training interruption.
ACT Model Training Guide
ACT (Action Chunking Transformer) is designed for single-task or short-sequence policy learning. While it falls short of smolVLA in multi-task generalization, it remains a cost-effective choice for scenarios with clear tasks, high control frequency, and relatively short sequences.
The ACT model requires policy.n_action_steps ≤ policy.chunk_size. It is recommended to set both parameters to the same value (e.g., 100) to avoid configuration errors.
Data Preprocessing Requirements
Trajectory Processing:
- Ensure uniform clip lengths and time alignment (recommended 10-20 step action chunks).
- Normalize action data to a unified scale and unit.
- Maintain consistency in observation data, especially camera intrinsics and viewpoints.
Training Configuration:
Local Dataset Training Example (Default Recommended)
DATASET_ROOT=~/Downloads/mylerobot3
lerobot-train \
--policy.type act \
--dataset.repo_id local/mylerobot3 \
--dataset.root ${DATASET_ROOT} \
--output_dir /data/lerobot_act_finetune \
--batch_size 8 \
--steps 100000 \
--policy.chunk_size 100 \
--policy.n_action_steps 100 \
--policy.n_obs_steps 1 \
--policy.optimizer_lr 1e-5 \
--policy.device cuda \
--policy.push_to_hub false \
--save_checkpoint true \
--save_freq 10000
Hyperparameter Tuning Recommendations:
- Batch Size: Start with 8 and adjust based on VRAM (ACT recommends smaller batches).
- Learning Rate: Recommended 1e-5; ACT is sensitive to learning rate.
- Training Steps: 100k-200k steps, adjusted based on task complexity.
- Action Chunk Size: Both
chunk_sizeandn_action_stepsare recommended to be set to 100. - Regularization: Increase data diversity or use early stopping if overfitting occurs.
Performance Tuning Strategies
Handling Overfitting:
- Increase diversity in data collection.
- Apply appropriate regularization techniques.
- Implement early stopping strategies.
Handling Underfitting:
- Increase training steps.
- Adjust learning rate schedules.
- Check data quality and consistency.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Data Export Related
Q: How long does LeRobot data export take?
A: Export time primarily depends on data scale and current system load. Typically, it takes 3-5 minutes of processing time per GB of data. For better efficiency, it is recommended to export in batches by task type instead of processing an oversized dataset at once.
Q: What are the export limits for the free version?
A: The free version has reasonable limits on the number and frequency of exports per user, which are displayed in the export interface. For large-scale data export, it is recommended to upgrade to the paid version to enjoy unlimited exports and GPU acceleration.
Q: How can I verify the integrity of exported data?
A: Use LeRobot's built-in validation tool to check:
python -m lerobot.scripts.validate_dataset --root /path/to/dataset
Q: What if the exported dataset is too large?
A: You can optimize it through:
- Reducing the export frequency setting (default 30fps can be reduced to 10-15fps).
- Splitting the export by time segments or task types.
- Compressing image quality (while ensuring training effectiveness).
Data Visualization Related
Q: What if Rerun SDK installation fails?
A: Please check the following conditions:
- Ensure Python version ≥ 3.10.
- Check if the network connection is stable.
- Try installing in a virtual environment:
python -m venv rerun_env && source rerun_env/bin/activate. - Use a local mirror:
pip install -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple rerun-sdk==0.23.1.
Q: Does online visualization require data to be public?
A: Yes. The online visualization tool on Hugging Face Spaces can only access public datasets. If your data contains sensitive information or needs to remain private, please use the local Rerun SDK solution.
Q: How do I upload data to Hugging Face?
A: Use the official CLI tool:
# Install Hugging Face CLI
pip install -U huggingface_hub
# Login to account
huggingface-cli login
# (Optional) Create a dataset repository
huggingface-cli repo create your-username/dataset-name --type dataset
# Upload dataset (repo_type specified as dataset)
huggingface-cli upload your-username/dataset-name /path/to/dataset --repo-type dataset --path-in-repo .
Model Training Related
Q: What are the supported model types?
A: LeRobot format supports multiple mainstream VLA models:
- smolVLA: Suitable for single-GPU environments and rapid prototyping.
- Pi0: Powerful multi-modal capability, suitable for complex tasks (part of the OpenPI framework).
- ACT: Focuses on single-task optimization with high action prediction accuracy.
For specific supported models, please refer to: https://github.com/huggingface/lerobot/tree/main/src/lerobot/policies
Q: What should I do if I encounter out-of-memory errors during training?
A: Try the following optimization strategies:
- Reduce batch size:
--batch_size 1or smaller. - Enable mixed-precision training:
--policy.use_amp true. - Reduce data loading threads:
--num_workers 1. - Reduce observation steps:
--policy.n_obs_steps 1. - Clear GPU cache: add
torch.cuda.empty_cache()in the training script.
Q: How do I choose the right model?
A: Choose based on your specific needs:
- Rapid Prototyping: Choose smolVLA.
- Complex Multi-modal Tasks: Choose Pi0 (requires OpenPI framework).
- Resource-constrained Environments: Choose smolVLA or ACT.
- Single Specialized Task: Choose ACT.
Q: How is training effectiveness evaluated?
A: LeRobot provides various evaluation methods:
- Quantitative Metrics: Action error (MAE/MSE), trajectory similarity (DTW).
- Qualitative Evaluation: Success rate on real robot tests, behavior analysis.
- Platform Evaluation: EmbodiFlow platform provides visualized model quality assessment tools.
Q: How long does training take?
A: Training time depends on several factors:
- Data Scale: 50 demonstration clips typically take 2-8 hours.
- Hardware Configuration: A100 is 3-5 times faster than consumer-grade GPUs.
- Model Selection: smolVLA trains faster than ACT.
- Training Strategy: Fine-tuning is 5-10 times faster than training from scratch.
Technical Support
Q: How can I get help with technical issues?
A: You can get support through the following channels:
- Refer to official LeRobot documentation: https://huggingface.co/docs/lerobot
- Submit an issue on GitHub: https://github.com/huggingface/lerobot/issues
- Contact the EmbodiFlow platform technical support team.
- Participate in LeRobot community discussions.
Q: Does the EmbodiFlow platform support automatic model deployment?
A: Yes, the EmbodiFlow platform supports automatic deployment services for mainstream models such as Pi0 (OpenPI framework), smolVLA, ACT, etc. Please contact the technical support team for deployment solutions and pricing information.
Related Resources
Official Resources
- LeRobot Studio (EmbodiFlow Online Visualization): https://io-ai.tech/lerobot/
- LeRobot Project Homepage: https://github.com/huggingface/lerobot
- LeRobot Model Collection: https://huggingface.co/lerobot
- LeRobot Official Documentation: https://huggingface.co/docs/lerobot
- Hugging Face Online Visualization Tool: https://huggingface.co/spaces/lerobot/visualize_dataset
Tools and Frameworks
- Rerun Visualization Platform: https://www.rerun.io/
- Hugging Face Hub: https://huggingface.co/docs/huggingface_hub
Academic Resources
- Pi0 Original Paper: https://arxiv.org/abs/2410.24164
- ACT Paper: Learning Fine-Grained Bimanual Manipulation with Low-Cost Hardware
- VLA Review Paper: Vision-Language-Action Models for Robotic Manipulation
OpenPI Related Resources
- OpenPI Project Homepage: https://github.com/Physical-Intelligence/openpi
- Physical Intelligence: https://www.physicalintelligence.company/
Community Resources
- LeRobot GitHub Discussions: https://github.com/huggingface/lerobot/discussions
- Hugging Face Robotic Learning Community: https://huggingface.co/spaces/lerobot
This document will be continuously updated to reflect the latest developments and best practices in the LeRobot ecosystem. If you have any questions or suggestions, please contact us through the EmbodiFlow platform technical support channels.